California passed Proposition 24 on Tuesday, expanding the state’s existing privacy laws to make it harder for companies to collect your data.
Security Friday
Marijuana Website ‘GrowDiaries’ Exposed User Data
GrowDiaries is a social media platform for marijuana growers. Two of its servers leaked user data like usernames and passwords.
HP Print Drivers Slash Malware – TMO Daily Observations 2020-10-27
John Martellaro joins host Kelly Guimont to discuss a technical issue that causes HP printer drivers to appear on your Mac as malware.
Zoom Rolls Out End-to-End Encryption for Video Calls
Starting next week, video conferencing app Zoom is finally adding end-to-end encryption to its platform.
Zoom’s E2EE offering uses public key cryptography. In short, the keys for each Zoom meeting are generated by participants’ machines, not by Zoom’s servers. Encrypted data relayed through Zoom’s servers is indecipherable by Zoom, since Zoom’s servers do not have the necessary decryption key. This key management strategy is similar to that used by most end-to-end encrypted messaging platforms today.
Good to see Zoom doing this; they’ve certainly had misses in the past. Update: The new version is now available for most users.
Security Friday, Halide Mark II – TMO Daily Observations 2020-10-23
Andrew Orr joins host Kelly Guimont for Security Friday news and updates, and a look at Halide Mark II just in time for iPhonemas Day!
Examining the Feud Between Apple and Facebook
James Titcomb has a op-ed in The Sydney Morning Herald where he pieces together the Apple-Facebook feud.
Over the past six months Facebook has become Apple’s chief antagonist, airing its gripes with investors, the media, its own employees and even the regulators writing the rules that will govern digital services for the next decade.
That is despite the companies not being traditional rivals: Apple sells hardware and runs subscription services; Facebook gets 98 per cent of its income through advertising.
I think the fundamental difference is that Facebook is doing everything in its power to become a mediator for reality. But so far it’s a mediator on platforms that it can’t control, and Apple is chipping away at some of the tools Facebook relies on, like targeted advertising.
Thousands of Law Enforcement Agencies Use Phone Cracking Tools
Upturn, a non-profit focused on the use of technology by police, used over 110 public records filed with law enforcement departments across the country to figure out how many of them use phone cracking tools, or mobile device forensic tools (MDFTs).
Based on 110 public records requests to state and local law enforcement agencies across the country, our research documents more than 2,000 agencies that have purchased these tools, in all 50 states and the District of Columbia. We found that state and local law enforcement agencies have performed hundreds of thousands of cellphone extractions since 2015, often without a warrant.
Kelly and I will definitely share our thoughts in this week’s Security Friday.
How Homeland Security Caught Suspect in R. Kelly Case
A recently revealed warrant in the R. Kelly case revealed how U.S. Homeland Security used a Google search warrant.
Homeland Security special agent Sylvette Reynoso testified that her team began by asking Google to produce a list of public IP addresses used to google the home of the victim in the run-up to the arson. The Chocolate Factory complied with the warrant, and gave the investigators the list.
As we discussed on Security Friday today, it’s cool that law enforcement was able to do this, yet simultaneously scary since it involved a dragnet of Google users.
Security Friday, New iPhone Prepping – TMO Daily Observations 2020-10-16
Andrew Orr joins host Kelly Guimont for Security Friday news, The Week In Data Breaches, and tips for a seamless transfer to a new iPhone.
Barnes & Noble Hack Revealed in Emails to Customers
A Barnes & Noble hack occurred on Saturday, October 10, customers learned in an email from the retailer. Data that was accessible included email addresses, billing/shipping addresses, and telephone number. Financial data like credit cards were safely encrypted.
According to Barnes & Noble’s Nook Twitter account, a “system failure” was responsible for the service interruption for Nook owners. The firm said it was “working urgently to get all NOOK services back to full operation. Unfortunately it has taken longer than anticipated, and we sincerely apologize for this inconvenience and frustration.”
Security Friday! News Roundup and Location Data – TMO Daily Observations 2020-10-09
Andrew Orr joins host Kelly Guimont to discuss the latest news for Security Friday, and talk about location data on iOS and why it matters.
Apple’s Internal Networks Were Hacked for Three Months
But don’t worry, they were hacked by good guys working under Apple’s bug bounty program. Sam Curry, Brett Buerhaus, Ben Sadeghipour, Samual Erb, and Tanner Barnes found a total of 55 vulnerabilities.
During our engagement, we found a variety of vulnerabilities in core portions of their infrastructure that would’ve allowed an attacker to fully compromise both customer and employee applications, launch a worm capable of automatically taking over a victim’s iCloud account, retrieve source code for internal Apple projects, fully compromise an industrial control warehouse software used by Apple, and take over the sessions of Apple employees with the capability of accessing management tools and sensitive resources.
When I first saw the news I was aghast to learn that Apple only paid them US$55,000, but the blog post was updated to add that the team so far has gotten 32 payments totaling US$288,500. Still doesn’t seem enough to me. Apple needs to work on its internal security.
Privacy Advocates Call on Tim Cook to to Implement iOS 14 Privacy Features
Ranking Digital Rights, along with seven other organizations, sent a letter [PDF] to Apple CEO Tim Cook, urging the company to implement iOS 14 privacy features that are delayed until 2021.
Apple has the opportunity to reinforce its position as an industry leader on protecting the privacy of its users by empowering them to control who can track their online behavior. At the same time, this change can and should enable the company to become more transparent about how it enforces its terms against apps that violate its policies. By delaying the introduction of crucial privacy measures, the company is slowing the momentum it created.
DuckDuckGo Releases Driving, Walking Directions Powered by Apple’s MapKit
On Thursday privacy search engine DuckDuckGo announced new map tools that help people plan travel routes with walking and driving directions.
Organizations Using Both Mac and Non-Mac Devices Consider Apple Devices Safest Out The Box
More than three-quarters of organizations that use both Mac and non-Mac devices consider Apple’s offerings as the most secure out of the box.
IRS Investigated for Location Data Usage Without Warrant
The IRS is being investigated for its use of location data collected from apps without obtaining warrants.
The IRS’ attempts were not successful though, as the people the IRS was looking for weren’t included in the particular Venntel data set, the aide added.
But the IRS still obtained this data without a warrant, and the legal justification for doing so remains unclear. The aide said that the IRS received verbal approval to use the data, but stopped responding to their office’s inquiries.
Security Friday, Widgets, and You – TMO Daily Observations 2020-10-02
Andrew Orr joins host Kelly Guimont for Security Friday news and updates, and a discussion about iOS 14’s widgets and what they can/can’t do.
Can iOS 14 Widgets Steal Your Keyboard Info?
After claims that iOS 14 widgets are up to no good, can they access your keyboard and act as keyloggers? First, as the developer of Widgetsmith says:
Leaving for a moment that I don’t think that is technically possible for a widget to read the keyboard. Widgetsmith was built from the ground up with complete privacy in mind and collects essentially no data about its users.
After using the app I wrote about this morning, Sticky Widgets, I’d say yes they can access your keyboard, because if not then Sticky Widgets would be unusable and you couldn’t type anything into them. Can they access the keyboard without user consent? Most likely not, as the quote continues: “Widgets use SwiftUI views to display their content. WidgetKit renders the views on your behalf in a separate process. As a result, your widget extension is not continually active, even if the widget is onscreen.”
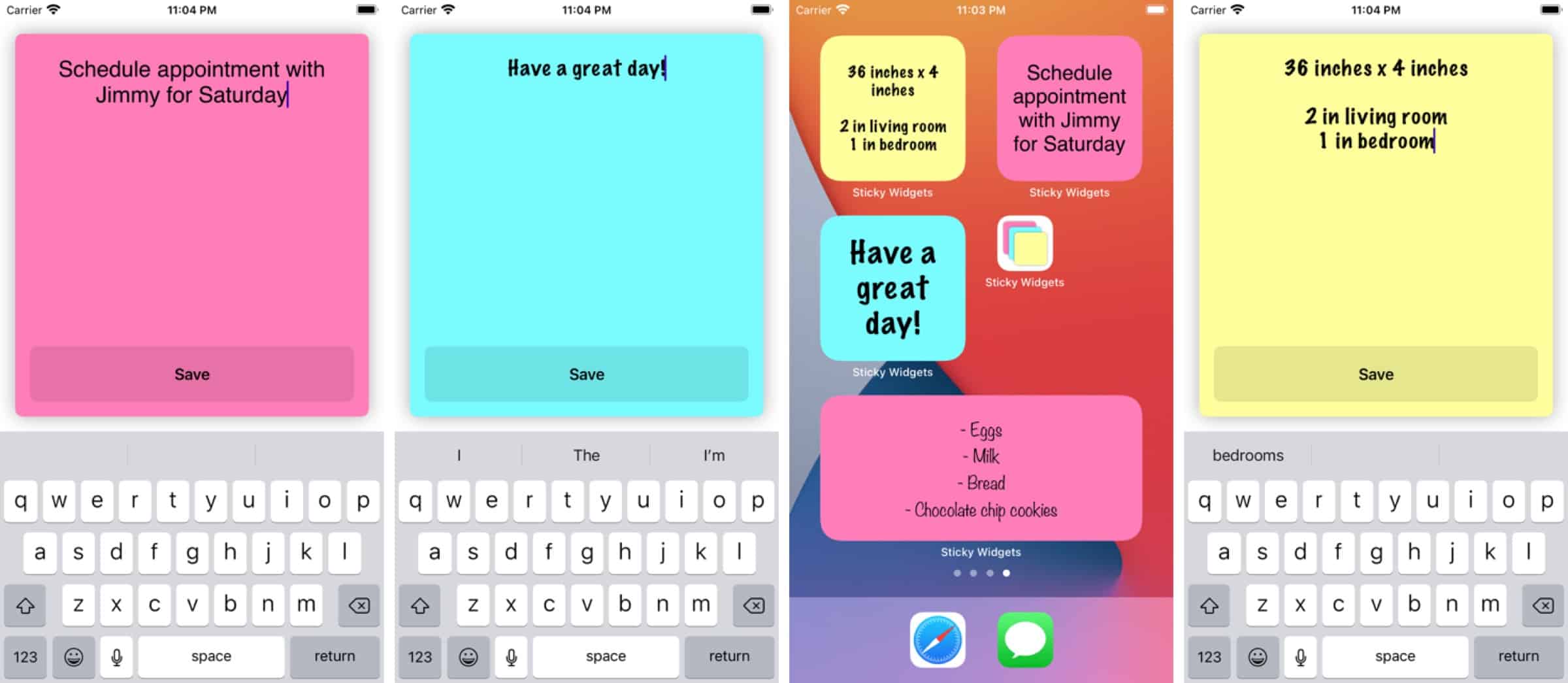
Put Sticky Notes on Your Home Screen With ‘Sticky Widgets’
Many Mac users have fond memories of Apple’s sticky notes widget and you can replicate that experience with Sticky Widgets. It lets you add sticky notes on your Home Screen in two steps: 1) Add a Sticky Widget to your Home Screen; 2) Tap on the widget to edit it. This is one app you should download immediately, although you probably don’t need me to tell you that since sticky notes on the screen are so useful. With these widgets easily accessible and in my face, I no longer have to create a reminder for stuff to get at the store, and a reminder to remind myself to set the other reminder.
Security Friday, Keychain Tips, Settings Shortcuts – TMO Daily Observations 2020-09-25
Andrew Orr joins host Kelly Guimont to discuss Security Friday news, tips for secure payment options, and some new shortcuts.
Here are 6 Advertising Trackers I Found on The Mac Observer
Like many websites, The Mac Observer uses advertising trackers and cookies. Here are six of them Andrew found using Safari 14.
Create iOS 14 Widgets With the “Widgetsmith’ App
Widgetsmith lets you create iOS 14 widgets and customize them to suit your needs and Home Screen theme. The app includes a variety of widget categories like weather, calendar, timezone converter, and others. Widgets can even by scheduled to appear on your screen following rules you define. App Store: Free (Offers In-App Purchases)
Security Friday, Safari, Watch Pulse Oximeter – TMO Daily Observations 2020-09-18
Andrew Orr and Jeff Butts join host Kelly Guimont to discuss Security Friday news, Safari updates, and the latest feature of Apple Watch.
Apple Gave FBI Access to Rioter’s iCloud Account
According to court documents, Apple gave the FBI access to a rioter’s iCloud account who was accused of setting police cars on fire in Seattle this summer.
As FBI officers were investigating a Seattle man suspected of setting police cars on fire, they turned to Apple for help […] Apple disclosed the name, email, phone number, and residential address associated with Jackson’s account, then subsequently granted the FBI access to the contents of Jackson’s account in response to a court-ordered search warrant.
Apple was served a lawful subpoena in regards to a lawful investigation, as it does frequently. But the main point is that it contrasts with claims from President Trump and A.G. Barr that Apple hinders investigations because they can’t unlock iPhones. Apple can’t do that, but if a person backs content up to iCloud, then it can be accessed.